OUR SERVICES
Electric Vehicle (EV) Solutions
Technology is evolving rapidly and we are at the precipice of the all-electric economy revolution. Electric Vehicles will play a major part in this transition and powering them will be a critical task in both residential and commercial applications. Middy’s have the expertise to show you how.

AC v DC Charging Modes
- AC Charging is controlled via internal inverter
- DC Charging is controlled via external inverter
EV Charging Levels
EV Charging Levels refers to the type of connection and speed of the charger.
- Typical Power Point 10A x 240V = 2.4kW - 10-14km of range per hour of charge.
- 7.4kW AC Charger - 32A x 240V = 7.4kW - 30-40km of range per hour of charge.
- 22kW AC Charger - 3 x 32A x 240V = 22.2kW - 100-120km of range per hour of charge.
- 25kW DC Charger - 35A x 415V x √3 = 25kW - 100-150km of range per hour of charge.
- 50kW DC Charger - 70A x 415V x √3 = 50kW - 200-300km of range per hour of charge.
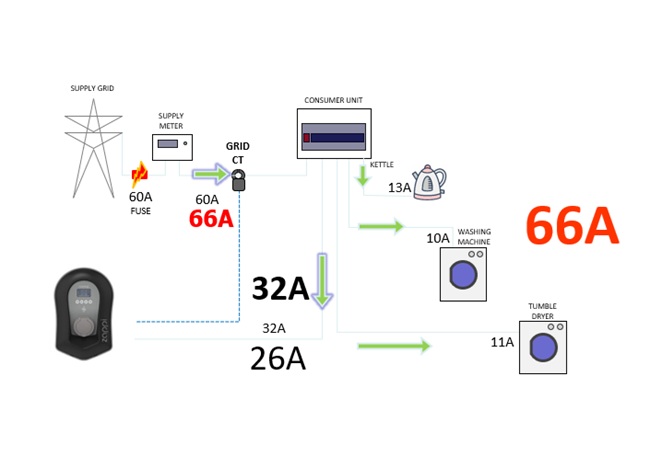
Dynamic Load Control & Balancing
Using smart chargers with CT units allows us to alter the load of the charger when there is not enough power.
Product Brochures
Products
Middy’s Branch Availability
Visit your local Middy’s branch today and talk to our staff for same day, expert advice for you and your customers . The EV range is available online and at 30 Middy's branches Australia-wide.
| VIC | NSW | NT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TAS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WA | |
|
ACT |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
SA | |
|
|
|
|
||
|
QLD | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Glossary of Terms
We’ve established a glossary of Electric Vehicle terminology to help you navigate your EV solution.
- AC Charging - Alternating current (AC) charging is typically how people charge their electric vehicles overnight. In that case, the EV has an on-board charger charging the battery, so the speed of charging depends on its speed. Typical maximum speeds of AC charge points are 7.4KWh, 11KWh and 22KWh.
- Connection - The connection of the EVSE to the EV charging infrastructure.
- DC Charging - Direct current (DC) charging for electric vehicles allows for higher charging speeds since DC can be supplied directly to the electric vehicle’s battery at power levels usually higher than AC charging. The higher the DC power supplied, the faster the electric vehicle can be charged—provided the EV is designed to handle such power.
- Demand Response - Demand response allows consumers to play a vital role in the electric grid operation by reducing or shifting their electricity consumption during peak times in response to time-based specific rates or other forms of financial incentives, offered by power utilities for balancing supply and demand.
- Electrical Capacity - The maximum power or electricity that can be delivered through a connection point, such as the incoming connection to a building or a dwelling, without a circuit breaker or fuse acting to cut the supply in order to protect the installation from fire. Power is calculated from the current which is measured in Amps and may be single phase or three phase.
- Electrical Supply Upgrade - An upgrade to the electrical supply to the building, including main distribution panels, for which costs vary markedly. In every case a separate quote is required from the distributed network service provider (DNSP).
- Energy Management System (EMS) - A computer-aided tool used by power system operators to monitor, control, and carry out optimal energy management. See also load control.
- EV Charging Station - EV supply equipment owned and installed on common property by the owners’ corporation for shared use; includes all supporting EV charging infrastructure.
- EV Charging Infrastructure - The connection from the main distribution board to a sub-board, distribution box or any other device the owners’ corporation has installed to facilitate the connection of EVSE to the common property electricity supply of the building. It includes load control, billing feeds and cable trays on common property to lots. EV charging infrastructure is normally common property and is owned by the owners’ corporation (OC).
- EV Operator or Charge Point Operator (CPO) - A company or organisation that provides EV charging services, including responding to quotes, installation, maintenance and billing; many provide a ‘turnkey’ solution.
- EV Supply Equipment (EVSE) - A device used to connect an EV into the building electricity system for the purpose of charging the EV; normally owned and supplied by an EV owner.
- GPO - “general purpose outlet”. An abbreviation for the standard 3-prong power plugs used throughout Australia
- Level 1 Charging - Charging from a GPO using a portable charging cable.
- Level 2 Charging - Charging from an AC charging station at home or in public. This method uses EV-specific plugs and stations and is usually at least 3x faster than level 1 charging.
- Level 3 Charging - charging from a DC charger. Stations of this size and speed are generally only available on select public networks or for commercial use. DC charging is incredibly powerful, delivering full charges in as little as 15 minutes
- Load Control - An approach or mechanism to ensure the peak electrical supply to the building is not exceeded, such as time shifting to off-peak, threshold control and demand management system (DMS). Includes energy management systems (EMS).
- OCCP (Open Charge Point Protocol) - An application protocol for communication between electric vehicle (EV) charging stations and central management systems, even when produced by different vendor.
- Peak Demand - The maximum power in a period that is or has been delivered through a connection point. This is usually measured in kVA (kilo-volt-amps). Peak demand has a significant impact on commercial energy bills. Additionally, if peak demand exceeds electrical capacity, various protection mechanism like circuit breakers or fuses activate which will cut the supply of electricity.
- RFID - a radio frequency card-based ID technology used to access public charging stations.
- Single Phase Power - The most common type of power, used in most residential households.
- Three Phase Power - More common in industrial areas but can also be found in some residential areas. It is capable of transferring more power to certain compatible EVs.
- Smart Charging - Smart charging is the ability to manage, monitor, and restrict EV charging to optimize energy based on local consumption demand. Typically, this refers to things like load balancing, energy monitoring and “managed charging”.
- State of Charge - SOC is the equivalent of a fuel gauge for the battery pack in an EV. The units of SOC are percentage points, with 0% meaning no charge left and 100% meaning fully charged. This allows you to see how much capacity is still available.
- Type 2 Plug/Socket - the Australian standard EV plug design. Utilises a 7-pin plug or socket for connection to charger and vehicle and is used by charging networks nationwide






